A benchtop solution for end-to-end automation of MALDI-TOF target plate preparation for bacterial identification
Introduction
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry is a critical tool for microbial identification. However, manual preparation of MALDI-TOF target plates is labour-intensive and prone to variability.
This report investigates the efficiency of using a SQWERTY liquid handling system to automate the formic acid and matrix handling steps of MALDI-TOF plate preparation.
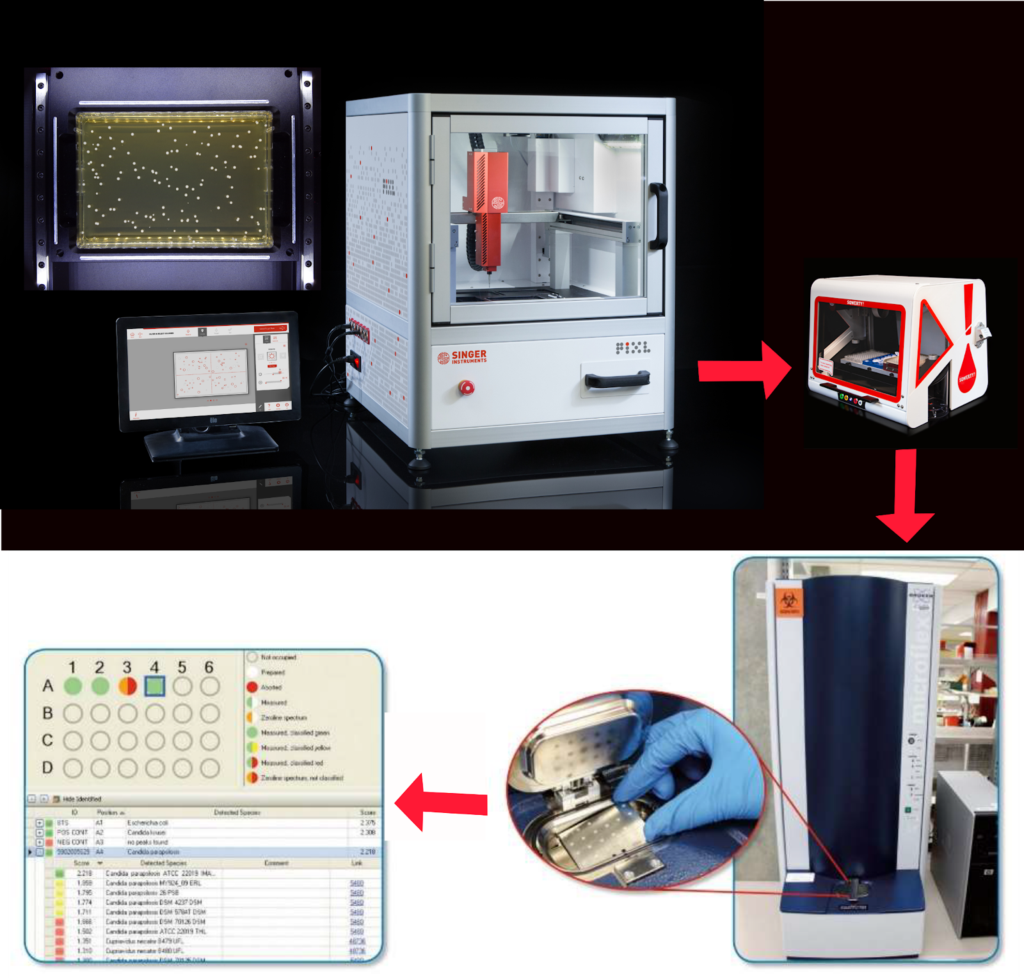
In a direct comparison with manual transfer methods, the use of PIXL to automate transfer of colony material to Shimadzu MALDI-TOF target plates has previously been shown to achieve 99.9% species identification confidence against the SARAMIS database across diverse organisms, along with fewer contaminants.
Combining PIXL with SQWERTY to automate both the colony transfer and liquid handling steps therefore provides a potential benchtop solution for achieving efficient end-to-end automation of MALDI-TOF plate preparation.

Results
The efficiency of SQWERTY for liquid handling was systematically assessed.
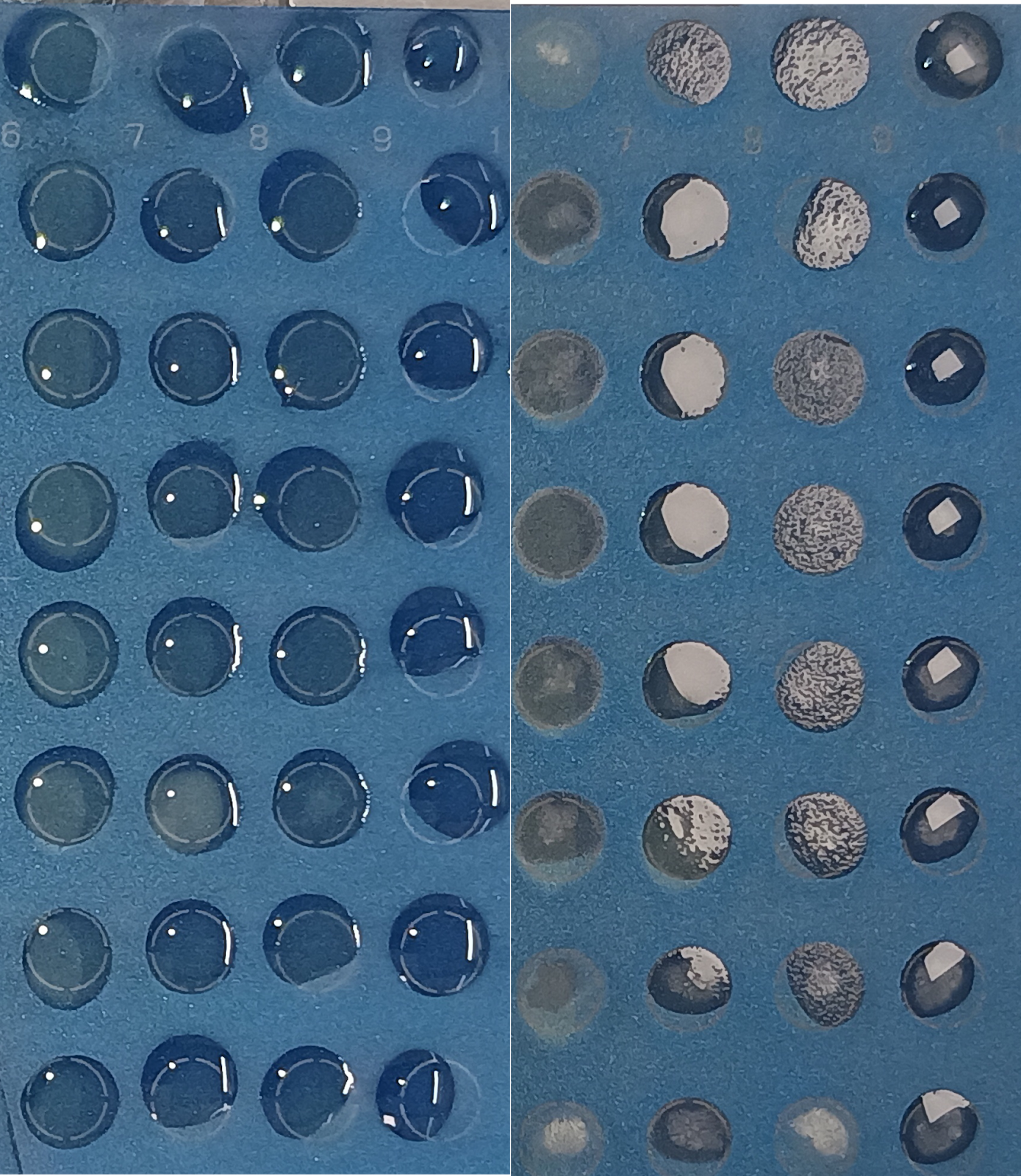
SQWERTY was used to dispense precise volumes of 1 μL of 85% formic acid and CHCA matrix solution onto the MALDI-TOF target plates. Although volumetric accuracy is subject to variations influenced by multiple factors (Guan et. al., 2023), SQWERTY demonstrated a 2.3% error rate when dispensing 10 μL of water. This level of precision compares favourably to manual pipetting techniques, which exhibited error rates of 5.7% when performed by an experienced user and 8% when performed by multiple users under comparable conditions, as documented by Lippi et al. (2016). A visual comparison of liquid droplet distribution, presented in Figure 2, reveals that the droplet sizes resulting from manual and automated liquid transfers onto a 96 MBT plate are visibly similar, suggesting a comparable level of volumetric accuracy.

SQWERTY demonstrated a positional error of ±0.125 mm, resulting in highly consistent and precisely aligned liquid deposition onto the target plates. Figure 3 illustrates the improved positional accuracy achieved by the SQWERTY compared to manual pipetting, showcasing the formation of clean, straight arrays of liquid depositions.
SQWERTY completed the 96-position liquid dispensing process within a timeframe of 6 to 7 minutes, which is comparable to the time required for manual pipetting.

Conclusion
SQWERTY provides a reliable and consistent alternative to manual pipetting for the loading of formic acid and matrix solution as part of MALDI-TOF microbial identification workflows. Observations indicated at least comparable volumetric and positional accuracy, with the additional benefits of enhanced reproducibility and walkaway time.
SQWERTY therefore provides a relatively affordable and efficient benchtop solution for labs wishing to automate the liquid handling steps of MALDI-TOF plate preparation that, together with a PIXL colony picker, could be used to achieve end-to-end automation MALDI-TOF plate preparation.
Method
1) Colony transfer with PIXL
A standard petri dish containing bacterial colonies was placed into the PIXL automated colony picking system, and the random colony picking workflow, pre-programmed within the PIXL software, was subsequently initiated. This resulted in the precise transfer of individual bacterial colonies from the petri dish onto a Bruker 96 MBT MALDI-TOF adapter plate.
2) Automated matrix application with SQWERTY
Following the colony transfer performed by PIXL, the Bruker 96 MBT MALDI-TOF adapter plate was removed from the PIXL system and transferred to the SQWERTY liquid handling system. The SQWERTY system was then configured with the necessary reagents, specifically 85% formic acid and CHCA matrix solution (10 mg/mL in 70% acetonitrile/30% water). The pre-defined MALDI-TOF workflow for the Bruker 96 MBT adapter plate, as depicted in Figure 4, was initiated via the SQWERTY software.
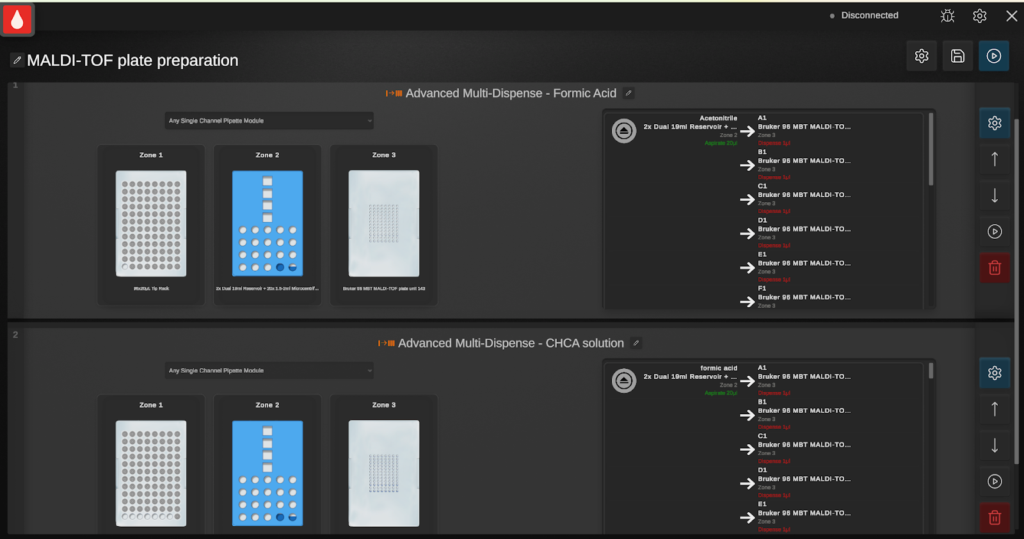
The SQWERTY workflow consisted of the following sequential steps:
- The SQWERTY system dispensed 1 μL of 85% formic acid to each designated position on the MALDI-TOF adapter plate.
- An air-drying or user-defined evaporation period was implemented to facilitate the evaporation of the formic acid.
- Following the evaporation period, the SQWERTY system dispensed 1 μL of CHCA matrix solution (10 mg/mL in 70% acetonitrile/30% water) to each designated position on the MALDI-TOF adapter plate.
- A crystallisation period was allowed to facilitate the formation of CHCA crystals onto the bacterial samples.
Following automated preparation by PIXL and SQWERTY, the MALDI-TOF target plates were ready for analysis by a Bruker MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer.
Need a bespoke MALDI-TOF automation solution?
Our product experts will collaborate with you to design a system tailored to your specific needs.